Infinite Hierarchical Nesting
of Matter
Introduction
The proposed theory Infinite Hierarchical Nesting of Matter is
a cosmological framework that suggests that matter can be divided or reduced
infinitely, as opposed to atomism. As such it lies in stark contrast to
standard model making it an alternative philosophical, physical and
cosmological theory. This concept is based on inductive logic and reaches
conclusions about structure of observed universe. Metaphysical schools studying
this theory focus on fundamental organizing principles of nature. Initial versions
of this theory were known as Discrete Fractal
Paradigm, and subsequently Discrete
Self-Similar Cosmological Paradigm .
Contents
|
Core claims of the theory
Discrete Self-Similar Cosmological Paradigm
focuses on nature’s fundamental organizing principles and symmetries. It
emphasizes nature’s hierarchical organization of systems from smallest
observable subatomic particles to largest superclusters of galaxies. It
introduces a paradigm which also highlights the theory that nature’s global
hierarchy is highly stratified into discrete scales or levels. Some of which we
can currently observe, such as Atomic, Stellar, and Galactic Scales. The third
primary principle of the paradigm is that cosmological Scales are universally
self-similar. Which indicates that for each class of objects or phenomena on
any given Scale there is analogous class of objects or phenomenon on every
other cosmological Scale. These parallel analogues from different Scales have
strongly analogous morphologies, kinematics and dynamics. [1]
From a purely physical point of view these similar relations lead to similarity
of matter levels and SPФ symmetry, which asserts invariance of
physical laws operating on different levels of matter.
Individual observations and claims
- In this theory there are no elementary particles
of matter (see preon, parton, electron, quark, Action/Reaction_Theory); instead it claims that matter is infinitely divisible. This claim
lies in contrast to the theory of atomism, which assumes existence of
units of matter that possess a minimum size.
- Universe consists of an infinite number of
enclosed levels of matter. Each level possesses characteristics similar to
each preceding level. This leads to a similarity of cosmic systems;
including similarity of shapes, sizes, masses, rates of processes, and
equations of motion.
- Each level of matter includes carriers with a
specific spectrum of sizes and masses. Additionally, matter is organized
in stable conditions and is under influence of fundamental forces and
interactions with objects of different systems.
- Distribution
of cosmic objects by levels of matter, which are steps of an infinite
hierarchy of cosmic systems, is carried out on the basis of geometric progression.
- The
passage of time, in terms of speed of similar events, is much faster at
the microlevel and slower at the macrolevel.
- Each type of "elementary" particles
(electrons, nucleons, etc.) does not
depend on strictly identical mass nor the size of particles.
- Universe
is eternal, while carriers of matter are constantly being born and then
transformed into carriers of their own and/or other levels. Thus, the
theory goes beyond not only atomism, but also Big Bang in cosmology, which
limits the history of universe to the moment of its creation.
- Dimensionality
of space-time is determined by structure of matter. Time in this theory is
a coordinate independent of space, which is a derivative of speed of
movement and development of matter. Four-dimensional space-time,
consisting of three spatial dimensions and time, is widely used in
science. The theory of infinite nesting
of matter proves existence of a fifth, scale
dimension.
- Action of forces of gravitation and electromagnetism can be
explained by a modified Le Sage's theory of gravitation. Objects of different levels of matter
generate radiation in form of fluxes of particles and field quanta, which
together lead to formation of fundamental forces acting on objects of
other levels of matter. It is possible that gravitational field is also a
specially ordered electromagnetic field of underlying level of matter and
is reduced to action of charged particles of vacuum field, which is the
content of electrogravitational vacuum. [2] [3]
[4] [5]
- There is a difference between concepts of
"quantity of matter" and gravitational mass, implying that under
certain conditions, different amount of substance may possess the same
gravitational properties. This follows from dependence of gravitational
forces on velocity of bodies, and from dependence of gravitational mass of
a body on density of substance of this body, which in turn depends on
speeds of motion of particles of the body. [6] [7]
- Inertial
mass as a
measure of inertia on the level of elementary particles is determined by strong
gravitation,
and at the macro level – standard gravitation, and is a function of amount
of interactions of particles of vacuum field with matter. [8] [9]
From point of view of field theory, all fields present in physical system
contribute to inertial mass of the system. [10] [11]
- Distribution of systems consisting of living
beings among cosmic systems have the same laws inherent to systems with
non-living matter. [12]
Historical
background
Quotations
of famous philosophers and scientists
- That matter is divisible to infinity was claimed
by Aristotle, Descartes, and also Gottfried Leibniz [13]
in his monadology.
- Isaac Newton wrote: "Nature is very similar to itself and is very simple,
performing all the great movements of celestial bodies with the help of
attraction, gravity ... and every small particle motion of these bodies –
with the help of other attractive and repulsive forces binding particles."[14]
- In each particle, no matter how small it is,
"there are the cities occupied by people, cultivated fields, and the
sun, the moon and other stars like ours" – claimed the Greek
philosopher Anaxagoras in his work on gomeomeriya in V century BC.
The famous Russian
poet Valery
Bryusov. [15] said:
"Perhaps, these electrons
Are the Worlds, where five
continents,
Arts, knowledge, wars, thrones
And memory of forty centuries!"
As Above So
Below
Quod
est inferius est sicut quod est superius
- This principle first uttered more than two
thousand years ago, has been accepted as an axiom by followers of hermetic
religious philosophy. From times of late antiquity, the Hermetic
traditions began mystery schools from which, in Middle Ages alchemical
science and other forerunners of modern mystery schools were born: notable
groups being illuminatus, frank-macons, and rosicrucians.
- Many of foremost scientists of Middle Ages and
present day have been connected with any of these movements, mainly
because these organizations kept to themselves information inaccessible to
any other. Hermetic scholars proposed the parallels between microcosm and
macrocosm: in a religious sense, this analogy was understood as conformity
to God with man created in his image and possessing similar divinity.
However in science the statement about structural parallelism can be
understood much more widely.
- Modern
science increasingly confirms the truth and fundamentality of postulates
set out in ancient philosophical texts. In
particular, theory about similarity of processes occurring on both
macro-and microlevels, is consistent with Hermetic belief. Study of
extraordinary people's ideas lead to the same conclusions. Great
researchers such as Leonardo da Vinci, possessed an uncanny ability to
simultaneously perceive the whole and its parts; the principle of his
research play prominently in analysis of and division of phenomena into
improbably small components then to their synthesis in new configurations.
Da Vinci designed the pyramid schema of mechanics, according to which: All
natural forces – which he called the "four forces" – movement,
mass, force and collision – are based on the system of the pyramids and
follow naturally from one another. This principle
of pyramid in which energy gathers and is then lost in a
geometrical proportion, has been made a basis of mechanics. Albert
Einstein's "Unified Field Theory" was aimed at establishing a
correspondence between essence of all physical phenomena in Universe –
from space-time up to atom.
- On the other hand, inherent metaphorical
qualities, in particular, the statement of Hermes about general
parallelism, is the primary mode of thinking of pathbreakers and authors
of ancient texts. “I wish to know ideas
of the God, all rest – is details”, Einstein wrote. The central
propositions on which the science is based, this aspiration to accuracy
and unambiguity, also appear metaphorical.
This axiom
regarding the similarity of all real communication between science, philosophy,
and religion lies unchanged.
Philosophical
underpinnings
Kant and Lambert
In cosmological representations of
Immanuel Kant there was a recognition of existence of uncountable sets of star
systems which could be united into systems of a higher order. At the same time
each star with their planets and satellites forms a system of subordinated
order. "The Universe, hence, not only
is spatially infinite, but also structurally diverse, as its structure includes
space systems of different orders and sizes." Putting forward
this position, Kant came nearer to idea about structural infinity of Universe
which has received fuller development in cosmological doctrine of contemporary
of Kant, German scientist Johann Heinrich Lambert in 1761. Baruch Spinoza was
an adherent of Infinite hierarchical model of Universe.
Fournier
D'Albe
Irish scientist Edmund Edward Fournier D'Albe has made the assumption, that hierarchical ladder also
extends into matter, in direction of decreasing. [16] According to Fournier D'Albe, a denominator of progression, that
is, ratio of linear dimensions of a star and an atom, is expressed by number 1022. Fournier D'Alba called the metagalactic level of
matter the supra world, and he called the nucleonic level of matter the infra
world. For an observer of the supra world, there are its own stars, with the
size of metagalaxies, and its own atoms, with the size of the Sun and other
stars, and ratio of their sizes is the number 1022. Such parity of spatial sizes Fournier D'Albe
distributed for time too. One second in our world in opinion of Fournier
D'Albe is equivalent to hundreds of trillions
of years in infra world, and a second in supra world is equal hundreds trillions of our years. Konstantin Tsiolkovsky was familiar with works of Fournier D'Albe.
Scientific
analysis
Infinite Universes and photometric paradox of Olbers
Model of hierarchical
structure of Universe, developed by Carl Ludwig Charlier based
on idea of Johann
Heinrich Lambert, was
used to explain photometric paradox within the framework of classical cosmology[17] In
1908, Charlier published a theory of structure of Universe, according to which
Universe is an infinite set of systems of increasing complexity that are
included in each other. In this theory,
individual stars form a galaxy of first order, a set of galaxies of first-order
forms a galaxy of second-order, and so on to infinity. Based on this idea of
structure of Universe, Charlier came to conclusion that in infinite Universe
photometric paradox is eliminated if distances between equal systems are
sufficiently large compared to their sizes. This leads to a continuous decrease
in average density of cosmic matter as we move to higher-order systems. For
elimination of paradox it is required, that mass density fall more quickly,
than in inverse proportion to a square of distance from observer. Such
dependence of density of matter in Metagalaxy is not observed, therefore modern
explanation of Olbers paradox is based on other principles (for example, red shift, general relativity
and so on). However, the very idea of complex structure of Universe and nesting
of systems of different levels remains and develops. Albert
Einstein and F. Selety discussed hierarchical model of Charlier in 1922 - 1924
years. [18]
Fractal
cosmology
According to
fractal cosmology, distribution of matter in cosmological systems occurs
according to a certain law, depending on size of systems, taking into account
principle of similarity occurring structures. Benoît Mandelbrot – in order to solve mathematical
theorem: about infinite
hierarchical (recursive) self-similar sets, for description of the given
systems creates a new term – fractal.[19]
Cosmological and philosophical views of Mandelbrot in historical aspect are
well described in his unpublished paper " Two heirs to the Great Chain of
Being " [20] and in book of Yurij Baryshev and
Pekka Teerikorpi . [21] Baryshev applies fractal
cosmological model with fractal dimension D = 2 in order to interpret redshift
of galaxies as a result of gravity. This model with the help of dark matter can
explain observed large-scale distribution of matter and associate it with
background radiation. [22]
Experimental
results
In 1937, Paul Dirac
suggested that parameters of large cosmological systems can be connected with
parameters of elementary particles with the help of some large coefficients. [23] Hypothesis of large numbers was also considered by
Hermann Weyl, [24] Arthur Stanley Eddington, [25] Oskar Klein, Pascual Jordan and others.
Gérard de
Vaucouleurs in 1970 used hierarchical model to describe changes in density of
galactic systems, depending on their characteristic size. [26]
Idea of nesting of matter was also considered by M.A. Markov [27] and D.D. Ivanenko (maximon - hadron - Metagalaxy). [28]
In 1978 Abdus Salam suggested
that hadrons could be regarded as microuniverses in de Sitter space, with action of strong gravitation. [29]
Well known
supporters
Hierarchical model of Universe is supported
by large group of scientists: from Italy, among which Erasmo Recami, P.
Caldirola, P. Castorina; Brazilian scientists W.A. Rodrigues, J.M. Martınez, V.
Tonin–Zanchin, Slovak scientist M. Pavsic; A. Neil from U.K./Denmark; Indian
scientists P. Ammiraju, K.P. Sinha, C. Sivaram, and others. They view
elementary particles as microuniverses inside, [30]
and outside such objects like black holes. [31] [32] In this regard, hypothesis of large numbers was
again considered. [33]
In
addition to application of ideas of general relativity to describe objects in
microworld, another trend has emerged: use of quantum approach to predict the
most probable orbits of planetary systems of stars. A review of some results is
given in the article Quantization of
parameters of cosmic systems.
Gaining
popularity
In the late 1970s and 1980s, the
idea that infinite nesting of matter was not only useful for explaining
individual phenomena and making connections between micro and macrocosm, but
that it could become a new scientific paradigm became increasingly widespread. [34] [35] [36]
Another name for
this paradigm — Discrete Self-Similar Cosmological Paradigm. [37] It implies similarity between infinite numbers of
discrete matter levels, and this
cosmological paradigm assumes a unified description not only of large
cosmological systems (stars, galaxies, metagalaxies, etc.), but also of
smallest objects – molecules, atoms, elementary particles, etc. Due to this
widespread support, in Russia, the theory of infinite nesting of matter is
considered a full fledged theory in systems
science and systems
theory, which are intended to describe cosmic
systems, their origin and evolution.
In
presented cosmological paradigm, formal limitation of atomism on theoretical
and experimental study of levels of matter that make up elementary particles is
completely abolished. Infinite hierarchical nesting of matter claims
unacceptability of general theory of relativity to describe entire Universe,
and precludes Big Bang as a likely scenario of Universe's development. In
addition, study of universal mechanisms of object formation, emergence of
fields and forces, their origin and interaction at different levels of matter
in infinite Universe is of great importance. An important result of the theory
was substantiation of fifth, scale
dimension of
space-time.
Generalization and
systematization of facts accelerated significantly at the beginning of 21st
century thanks to artificial satellites, modern observation tools - infrared
telescopes and computer analysis of accumulated material, as well as deepening
of knowledge in the field of elementary particles. Main attention of the
authors listed below was directed to formulation of theory of infinite nesting
of matter as an independent and necessary area of research for further progress
of science.
Further
research
Robert L. Oldershaw

Robert L. Oldershaw
[7],
independent researcher of college Amherst (Massachusetts, USA) in a number of
works since 1978 developed models of cosmological self-similarity (The
Self-Similar Cosmological Model). He has allocated three basic levels of matter
– nuclear, star and galactic levels. According to his work, matter is
concentrated to the given levels, basically in form of nucleons and stars, and
stars also in majority are a part of galaxies. [38]
[39] Oldershaw remarks, that overwhelming quantity
of matter in space contains in lightest elements – hydrogen and helium, and at
the level of stars – in dwarf stars with masses ranging between 0.1 – 0.8 solar
masses. Besides
this, there are many other examples of similarity:
- Rotation of carriers near each other under action
of a force, decreasing inversely proportional to square of
distance.
- Often observable jets and emissions of matter of
identical types form in stars and galactic systems.
- Ratio
of sizes of largest atoms to size of nucleon is of the same order as ratio
of size of large stellar systems to size of a neutron star.
- Dependencies between spin and mass, between
magnetic moment and spin have identical form at nuclear and star systems.
- Rydberg’s atoms exhibit
a relationship between radii and periods of oscillation of electron that
is very similar to Kepler's law for planets.
Oldershaw
determines coefficients of similarity in mass, size, and time of processes
between atomic and stellar systems by comparing the Solar System and Rydberg
atom with orbital number n = 168. In this case, hydrogen corresponds to stars
with masses of about 0.15 solar masses. Additionally he claims the
coefficients of similarity, in size and time are considered equal to each other
and have the value of Λ = 5.2∙1017 , and coefficient of
similarity in mass has the form ΛD = 1.7∙1056,
where exponent D = 3.174 . As a result of such comparison it begins to be
possible to do exact predictions of mass and sizes of stars, galaxies, size of
proton, periods of rotation of galaxies, etc. Oldershaw believes that
elementary particles should be treated as charged and rotating black holes,
whose radius in the first approximation can be estimated from Schwarzschild
equation:
![]()
where ![]() is gravitation constant, acting on given
level of matter, and
is gravitation constant, acting on given
level of matter, and ![]() for atomic level,
for atomic level, ![]() for level of stars,
for level of stars, ![]() for level of galaxies.
for level of galaxies.
Assuming that strong gravitational
constant ![]() m3•s–2•kg–1, Oldershaw
calculates a matching radius of an electron being 4∙10-19 m, and
radius of proton 0.81∙10-15 m. Stars and galaxies are assumed also
to be objects like electrons and protons. In particular, at the level of stars,
black holes are attributed to electric charge with value of up to 1.5∙1018
C. At the level of galaxies globular clusters of stars correspond to an
electron. Galaxies then correspond to proton and the more massive atomic
nuclei. To estimate size of globular clusters and galaxies it then becomes
necessary to multiply radius of electron and radii of atomic nuclei by the
value of Λ2. As can be seen from this
comparison, there is no complete parallel, since black holes are only suspected
in some globular clusters and galaxies, but do not obscure these objects
completely. Therefore, for electron Oldershaw introduces concept of halo consisting
of tiny particles that form matter of electron. This halo surrounds centre of
electron, just as external stars in globular clusters surround nucleus of the
cluster. According to Oldershaw, dark matter should
consist of black holes.
m3•s–2•kg–1, Oldershaw
calculates a matching radius of an electron being 4∙10-19 m, and
radius of proton 0.81∙10-15 m. Stars and galaxies are assumed also
to be objects like electrons and protons. In particular, at the level of stars,
black holes are attributed to electric charge with value of up to 1.5∙1018
C. At the level of galaxies globular clusters of stars correspond to an
electron. Galaxies then correspond to proton and the more massive atomic
nuclei. To estimate size of globular clusters and galaxies it then becomes
necessary to multiply radius of electron and radii of atomic nuclei by the
value of Λ2. As can be seen from this
comparison, there is no complete parallel, since black holes are only suspected
in some globular clusters and galaxies, but do not obscure these objects
completely. Therefore, for electron Oldershaw introduces concept of halo consisting
of tiny particles that form matter of electron. This halo surrounds centre of
electron, just as external stars in globular clusters surround nucleus of the
cluster. According to Oldershaw, dark matter should
consist of black holes.
Sergey I. Sukhonos
Sergey I. Sukhonos [8] in a number
of works [40] has shown existence of separate
material formations located on axis by 13 discrete groups through equal
intervals in logarithmic scale. Greatest discovered size belongs to Metagalaxy,
the least – to a hypothetical particle called maximon, some twenty orders
smaller then nucleon. Metagalaxies, nucleons, and maximons belong to basic
levels of matter. Between them, are all known objects whose properties
periodically repeat with ratio of sizes about 1022.
Sukhonos highlights fractal phenomena in nature, and also proves bimodality
when objects show supplementary properties: spiral and elliptic galaxies;
subdwarfs as primary stars of Galaxy with deficiency of heavy elements, and
usual stars of main sequence; external and internal planets; processes
of synthesis and division, monocentric and polycentric structures at different
levels of matter. For an explanation of specified laws Sukhonos utilizes ideas
about fourth, scalar dimension and corresponding interaction, and also wave
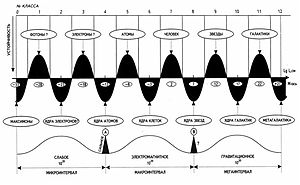
representations. With the help of “stability wave” scale axis is
divided into three major intervals − microinterval, macrointerval and
megainterval (the word “micro” here means “small”, not millionths).
Yun Pyo Jung
Yun Pyo Jung [9] from Korea criticizes theory of Big Bang in
connection with logical contradiction – on greater scales nearby space objects
never will make more than one orbit near each other because of the constant
expansion of the Universe, despite of gravitational communication between them.
Based
on the idea of recursive cosmology, by comparing sizes of galactic nuclei and
atomic nuclei, galaxies and atoms, clusters of galaxies and molecules,
coefficient of similarity in size is determined, with a value of approximately 1030.
The same value is deduced for coefficient of similarity in time, connecting
duration of similar processes in nuclear and galactic systems. [41]
Sergey G. Fedosin
Sergey G. Fedosin [10], the physicist and philosopher from Perm,
Russia, mathematically has successfully calculated basic features of the
theory, having passed from qualitative conclusions to quantitative results in
his monograph on theory of similarity. [42]
Eighteen
levels of matter from preons to metagalaxies were divided into basic and
intermediate according to their masses and sizes, and similarity ratios were derived between
them. The main scales in this range of levels of matter are the level of
elementary particles and the level of stars. At these levels there are many of
the most stable and long-lived carriers; such as nucleons and neutron stars
containing maximum quantity of composite particles and having maximum density
of matter and energy. Matter of these carriers is degenerate, so their
constituent particles are in quantum states with nearly the same energy, and
therefore states of such matter are described by the laws of quantum mechanics.
In this case a neutron star contains about Φ = 1.62•10 57 nucleons, and
by induction it can be assumed that the same quantum particles are contained in
nucleon. As a consequence of similarity of the atomic level and the level of
stars quantization of parameters of cosmic
systems is found.
Determination of coefficients
of similarity in mass Φ, in size P, and speed S, through duration of similar processes Π is made by means of hydrogen system. At the
level of atoms hydrogen system is a hydrogen atom, and at the level of
main-sequence stars − corresponding planetary system consists of a star of
minimum mass and a planet as analogue of electron. Degenerate compact stars
like white dwarfs and neutron stars possess their own coefficients of
similarity, based on ratio comparing parameters of proton. [43]
For magnetars as
analogues of proton electric charge with value of 5.5∙1018 C and
magnetic moment of 1.6∙1030 J / T are predicted.
Ratio of radius of
a neutron star to radius of a proton gives coefficient of
similarity of P = 1.4 •1019.
Total energy of a
neutron star without taking into account rest energy is defined by expression Es = MsC2,
where C= 6.8•107 m/s –
characteristic speed of
particles of the neutron star, Ms
– mass of the star. Similarly for a nucleon total energy En = Mnc2, where c = 2.9979•108m/s – speed of light and
characteristic speed of particles in matter of nucleon, Mn – mass of nucleon. Ratio of
speed C to speed of light c gives coefficient of
similarity on speed S = 0.23. Coefficient of
similarity on time is Π = P /S
= 6.1•1019. By calculation it then follows, that processes at the
level of nucleon matter proceed in Π time more
quickly, than at the level of neutron stars.
By comparing abundance of
stars of different masses with abundance of atomic nuclei, discreteness of stellar parameters and
one-to-one correspondence between chemical elements and stars are proven.
Theory of similarity predicts, that among stars the lightest are stars with
mass of 0.056 solar mass. Such stars are now discovered and are called brown dwarfs or
L-dwarfs. The Solar
System contains as many planets as an oxygen atom contains electrons. In
addition, the Sun's mass exceeds mass of lightest stars just as mass of an
oxygen atom exceeds mass of a hydrogen atom. The Milky Way Galaxy, together
with such galaxies as the Large Magellanic Cloud and the Small Magellanic
Cloud, form a cluster of galaxies similar in mass ratio to the water molecule H2O. Our
Galaxy is significantly more massive than the Magellanic Clouds and plays the
same role as oxygen atom in water molecule. Around of the given cluster of
three large galaxies are orbiting about 14 dwarf galaxies which can be named
galactic analogues of electron. Predicted values of typical
parameters of dwarf galaxies were also confirmed, with mass of 4.4 ∙ 106
solar masses and radius of up to 371 pc.[44] [45]
On both mass axis and size
axis, all natural bodies are arranged in discrete groups. Ratio
of mass between any of the next groups can be seen as the same number. Hence,
mass increase of objects occurs on a geometrical progression, the same is true
concerning sizes of objects. It allows an observer to compare coefficients of
similarity between various levels of matter and by that in advance to predict
still more about investigated badly objects. As a consequence, SPФ symmetry similarity
is proved between
basic levels of matter. An analogue of similar symmetry is CPT symmetry used in
quantum field theory.
In addition, Fedosin found a
connection between mass and energy of space objects, corresponding to
Einstein's formula (mass–energy
equivalence), identified stellar constants, such as stellar Planck constant, stellar Dirac constant and stellar Boltzmann constant, calculated
angular momentum and radius of the proton as well. [46] [47]
[48]
Explanation of red
shift in spectra of remote galaxies and cosmic microwave background radiation
from the concept of expanding Universe seems inadequate, and invites other
explanations. It leads to idea of cosmic red shift and microwave background
radiation as a consequence of interaction between photons and previously
unknown particles – nuons. At the level
of stars analogues of the nuons are white dwarfs, whose number exceeds number
of neutron stars. Fedosin shows that overall mass of nuons in Universe of the
same order as mass of all the known nucleons. Thus the problem of invisible
dark matter may be solved. A question must be raised about need for existence
of dark energy. In particular, effect of attenuation of radiation from distant
supernovas is considered to be consequence of scattering of photons on the
nuons, but not result of dark energy activity. [49]
Fedosin using Le Sage's theory
of gravitation based on the notion of gravitons derived formula for Newton's
gravity, found energy density and penetrating power of gravitons in matter, and
explained the origin of mass and inertia. [50] [8] In a
similar way he derived formula for Coulomb force between electric charges,
energy density and penetrability of charged particles of vacuum field in t
matter.[51] [3] Based on parameters of
particles of electrogravitational vacuum it was
possible to explain principle of operation of a spaceship engine that draws
energy from the vacuum. [52]
In order to describe nuclear
forces in gravitational model of strong
interaction he introduces concept of gravitational
torsion field and uses strong
gravitation, as constituent parts of strong interaction between elementary
particles. [53] Strong
gravitational constant which is equal to ![]() m3•s–2•kg–1,
can be calculated through coefficients of similarity between atomic and stellar
systems.
m3•s–2•kg–1,
can be calculated through coefficients of similarity between atomic and stellar
systems.
Idea of infinite
nesting of matter was basis for construction of substantial electron model and
explaining electronic spin. Substantial photon model
considers a photon consisting of praons, while neutrinos are assumed to consist
of graons. [54] Model
of quark quasiparticles shows that quarks can be
represented as a combination of two phases of hadronic matter and therefore,
they are quasiparticles. In this case, composition of hadrons can be reduced
to quarks only for the purpose of formally describing properties of hadrons,
and real reason for emergence of idea of quarks is discreteness and
quantization of properties of elementary particles and resulting symmetries of
their interactions in fundamental fields. In particular, in substantial neutron model and substantial proton model it is found that
mass of nucleons is in a narrow range of masses as a consequence of equation of
state of hadronic matter and its evolution in field of strong gravitation.
Electric charge of proton appears in reactions of weak interaction in neutron
matter during beta decay
and reaches a maximum when density of zero
electromagnetic energy becomes comparable to energy density of
strong gravitation. [2]
Analysis of electric and magnetic polarizabilities
of nucleons shows that they can be understood without invoking the idea of
quarks.
In concept of general field it is shown that
gravitational and electromagnetic fields, acceleration
field, pressure field, dissipation field, fields of
strong and weak interactions, and other force fields can be combined into one.
General field is universal in the sense that it operates at all levels of
matter and allows us to describe equation of motion of any object with the help
of one tensor equation. The article [55] shows that cosmological constant must have different values in
cosmic space, inside a neutron star and inside a proton. This allows us to
solve cosmological constant problem, arising in general theory of
relativity in Lambda-CDM model due to significant difference between density of
zero vacuum energy and observed value of rest energy density of matter in
cosmic space. Metagalaxy,
neutron star and proton, considered as relativistic
uniform system, turn out to be extreme objects in terms of the dependence
of their gravitational field on radius. [7]
Study of origin of
fundamental gravitational and electromagnetic interactions in articles [8] [3] leads to
following picture of disposition of basic levels of matter: level of graons –
level of praons – level of nucleons – level of stars – level of
supermetagalaxies. Distribution of material objects in Universe is described
with the help of scale dimension, which
extends over all levels of matter. Due to the similarity of matter levels, each basic
level of matter consists of objects of underlying basic level of matter. Hence
it follows that protons, neutrons, electrons, and all elementary particles
consist of neutral and positively charged praons
and negatively charged praelectrons. In turn, main components of praons must be
graons, in which smaller particles can also be found. This is how principle of
nesting of matter is realized and the substance is found that material objects
at all levels of matter are built of. This substance is a multicomponent
structure consisting of objects of basic levels of matter, which appear to be
the most dense and stable due to balance of corresponding fundamental forces.
Carriers of the substance are graons, praons, nucleons, neutron stars and other
similar objects with highest energy density.
Detailed
philosophical analysis of theory of infinite nesting of matter was carried out
by Sergey Fedosin in 2003. [56]
At each level of matter, characteristic basic carriers and boundary points of
measurement are allocated. Transitions from one level of
matter to another are carried out according to the law of transition of
quantity into quality, when number of carriers in an object exceeds permissible
limits of measure typical for a given object. Examples of fractal structures at
various spatial levels of matter are given. Due to hierarchical structure of
Universe, consisting of similar objects and field particles, repeatability of
elements of natural phenomena, unity and integrity of Universe is supported,
and symmetry of similarity are realized. Theory of infinite nesting of matter
is substantiated by the law of similarity of carriers of different scale
levels.
In
addition to infinite nesting of physical material objects of different levels,
an infinite nesting of living beings is also found.
Thus, within autonomous living organisms of one level, from the smallest prions
to whales, there are living structures of ever-decreasing sizes and lower scale
levels. At the same time, there is interpenetration of living and non-living matter,
and a clear correlation between sizes and masses of living carriers and
corresponding values of physical objects at different levels of matter. Nesting
of living matter in natural systems is manifested as distribution of organisms
of different species by scale levels according to masses and sizes, as well as
infinite internal nesting of levels of living structures in each individual organism.[12] As an
illustration, it is known, that in human body there is so much bacteria that
their total mass may be up to 0.2 kilograms. [11]
Infinite nesting of living
beings is in agreement with living
systems theory of James
Grier Miller, which considered many living
systems, in order of increasing size, and identifies his subsystems in each. [57] He
came to following conclusion: non-random accumulations of matter and energy in
physical space-time are organized into interacting, interdependent living
subsystems or components. In such complex structures, he identified eight
"nested" hierarchical levels, including a cell, organ, organism,
group, organization, community, society, and supranational system. Nesting is
understood here as the fact that an organ consists of many cells, and an
organism - of many organs, etc. In addition to such qualitative conclusions, in
the theory of infinite nesting, quantitative patterns are also determined using
similarity of matter levels. For example, coefficients of similarity by mass
are found, allowing one to estimate critical quantities of living entities that
differentiate between different levels of organization of life.
Tegmark M.
Max Tegmark
classifies different types of simultaneously existing universes, depending on
their possible properties. Under these universes he understands objects with
dimensions close to the size of our Metagalaxy. It is assumed that such
neighboring universes are autonomous and independent from each other, and they
may have even other physical laws, or other elementary particles and physical
constants. [58]
Leonard N. Plyashkevich, Mira L.
Plyashkevich
Leonard
N. Plyashkevich and Mira L. Plyashkevich in their work considered basic
postulates of a variant of cosmology, as an alternative hypothesis of Big Bang.
[59] The
authors attempted to identify a unified principle of structure of micro and
macrocosm. To achieve this goal, methods of transforming similarity and
dimensions of physical quantities are used. Gravitational field is considered
in terms of Faraday-Maxwell field.
Rejection of the Big Bang hypothesis and interpretation of red shift in spectra
of distant galaxies as Doppler effect allows for development of a hierarchical
model of Universe. Problem of coexistence of ordinary matter and antimatter is
mentioned. The purpose of the work is to demonstrate, without plunging into
abyss of metric theories, the right to existence and development a hierarchical
model.
Boris M. Sirotenko (Boris Antsis)
Unified structure of Universe.[60] About similarity micro-and a macrocosm.[61]
Salzman L.I.
Zaltsman
presented system of Universe, published in the book book
"Rise of the Worlds" (2003). [62] The system
covers the Being of both inert and living matter. The Universe is presented as
a dynamic hierarchy of particular Worlds. Daughter structures of inert matter
arise from elementary particles of parent structure by means of their
gravitational condensation in accordance with the theory of Jeans. It is
proved that only approximately half of the particles are involved in
condensation. The rest, having a high escape velocity, remain dispersed in
space and serve as material for a multitude of potential fields. It is proved
that substance of all particular Worlds, starting with microworld, acquires
properties of superfluidity, superconductivity, etc. The macroworld is
considered to be the last in already existing hierarchy. Scale constants are
given that connect sizes and masses of particles, as well as energy densities
and relaxation times of particular Worlds. It is proved that, despite the
infinite number of particular Worlds, all the basic parameters of Universe are
finite. Fundamental possibility of existence of life in each particular World
is proved, and it is considered why nature needed to create highly intelligent
creatures.
Leonard Malinowski
Leonard Malinowski coined the term
Scalativity (or Scale Relativity) to distinguish his approach from the work of
French physicist Laurent Nottale and his Scale
Relativity. According to Scalativity, there is no absolute level of
matter, all levels of matter are relative. An observer measures properties of
Universe relative to units of mass, size, and time chosen by him, which may be
taken by others and are therefore relative.
In Scalativity currently observable Universe and all its
contents such as particles (proton, neutron, electron, photon, neutrino),
cosmic objects (galaxies, stars, planets and so on ) and electric field lines,
are all presented as completely fractal. A truly Fractal Universe must
incorporate infinity completely into Physics as well as Scale Relativity, with
understanding that there must exist self-similarity levels
of matter. It is supposed that
neutron is composed of 1.2 x 1057 subquantum scale (sqs) Hydrogen
atoms; an electron is composed of 1.2 x 1052 sqs-Iron atoms with an
excess of 2.1 x 1040 sqs-electrons and a photon is composed of 4.5 x
1080 sqs-photons.
It is supposed that vast majority of stars are cosmic
scale nuclei in the process of cosmic scale (cs) beta decay. The sum of
electromagnetic and neutrino radiation emitted by a star over its life time is
one cs-antineutrino. Our Solar System is may be a cs-neutron in the process of
cs-beta decay. The iron/nickel cores of planets are expected to form one
cs-electron of mass 1.084 x 1027 kg. After
decay the Sun will be left with 2.1 x
1040 positive ions on its surface. The 2.1 x 1040 ionized
electrons will adhere to the cs-electron. The mass of mostly stable cosmic
scale nuclei should range from 1 solar mass to 238 solar masses.
According to Malinowski, Big Bang Universe is fractally
self-similar to a cosmic scale 500 Megaton Uranium 235 fission explosion.
Spiral galaxies are self-similar to nuclear explosion particles forming and
Elliptical galaxies are self-similar to drops of water in nuclear cloud
capturing many cs-neutrons.
With just two postulates, that the pre-solar system
mass is mass of a cosmic scale neutron and that a cosmic scale neutron is
composed of 100% Hydrogen atoms, Scalativity can calculate fractal chemical
compositions and binding energies of all nuclei. It is fascinating that to
obtain mass of the very stable nuclei Iron 56 by this method, one must fuse all
the quantum scale Hydrogen and quantum scale Helium available in 56 separate
protons and neutrons completely to 100% qs-Iron 56. There are many other quantum
scale - cosmic scale self-similarities identified at www.scalativity.com .
José Díez Faixat
In
several of his works José Díez Faixat reveals existence of a very precise
spiral rhythm in emergence of evolutionary leaps that mark the history of the
universe. [63] [64] [65] [66]
Fitting his ‘periodic table’
of rhythms to date of appearance of matter – Big Bang– and of organic life, he
find that every single instant of emergence of successive taxonomic degrees of
human phylogeny is marked out with absolute precision: Kingdom: animal, Phylum:
chordata, Class: mammal, Order: primate, Superfamily: hominoid, Family: hominid
and Genus: homo. The same then occurs with all the stages of maturation of our
primitive ancestors: H. habilis, H. erectus, archaic H. sapiens, H. sapiens and
H. sapiens sapiens. Once more, precision of the hypothesis is repeated in
successive transformations that humanity has experienced in its more recent
history: the Neolithic, Antiquity, the Middle Ages, the Modern Age and the
emergent Postmodern Age. The ‘periodic table’ of rhythms may also provide the
key to glimpse the successive phases yet to be deployed in the years to come in
an ever-accelerating process that will eventually lead to a moment of infinite
creativity –Omega– within a couple of centuries.
This
same hypothesis, which accurately describes the processes of global evolution,
also accurately describes development of an individual human being. Again, the
same models of unfolding and folding are used, passing through the same phases
of development. At the same time, the ‘periodic table’ of rhythms marks, step
by step, the nodal points of embryology. This confirms the old idea of
phylogenetic and ontological parallelism, supported by many psychologists and
various scientists, and gives an example of a fractal and holographic universe.
Cosmology of Raël
Raelian cosmology is based on similar
cosmological sights at the structure of Universe.
Theory in pop culture
- YouTube|cNV9FEKi9FQ|Intro
to cartoon serial Simpsons – The Ziff Who Came to Dinner. The episode the
first time is shown 14.03.2004 (to the 125 anniversary from the date of
Albert Einstein's birth).
- The ending of film of
Stephen Spielberg " War of the worlds " (War of the worlds,
2005) – http://www.imdb.com/title/tt0407304/
- Song Moby – We are
all made of stars, 2002
- The Dark Tower – a
series of novels of Stephen King
- Final in film "
People in black " (1997) / Men
In Black – one of the best screen versions of given article.