The electron-ionic model of
ball lightning was represented by Sergey G. Fedosin [1],
a physicist and the philosopher from Perm, Russia, and Sergey A. Kim, from Perm
state university, in a number of works. [1] [2]
In this model, ball lightning is
a cluster of the very hot ionized air with the positive charge in general,
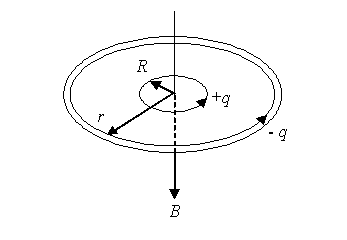
whose shell consists of the rapidly revolving electrons with the total current
up to 1,4•105 A. Ball lightning as whole is supported by the balance
of the electromagnetic forces, which act between the charges. Positive ions
inside the lightning are distributed freely as a result of the spherical
symmetry, and attract to themselves the electrons of shell, retaining them from
the dispersion. According to the model the ball lightning is formed from two
close branches of a linear lightning at the time of termination of current in
the main channel with the subsequent closure of branches in a current ring.
Electronic currents in the shell
create strong magnetic field inside the lightning. These currents are
perpendicular to rotational axis, the diameter of rotation decreases to the
poles, where magnetic field grows. This retains positive ions from the dispersion
along the rotational axis due to the effect of magnetic bottle. Basic magnetic
field inside the lightning is directed along the rotational axis. I.e., ions
can move along the axis along the lines of magnetic field. From other side, the
ions revolve in the circle perpendicularly to axis under the action of Lorentz
force with respect to their thermal velocity. As a result at a certain distance
from the axis of lightning appears the intersection of two ion flows, which is
observed as the luminous shells inside the lightning. Emission from the shells
appears from friction and recombination of the being intersected ion flows.
Theory predicts from the first
principles the maximum diameter of ball lightning 34 cm. [2]
With the larger size the summary charge of lightning, which has positive sign,
grows to the value of 10 –5 C and appears the electrical breakdown
of air near the lightning. The energy of the lightning in this case reaches
10.6 kJ, the current in the shell 1.4∙10 5 A, the internal magnetic
field of 0.5 Tesla. Because of its charge ball lightning does not simply float
under the action of the force of Archimedes, but it is retained by electric
force from clouds and the induced charge on the Earth. The formula for the
maximum radius of ball lightning has the form:
![]()
Where m, q are the electron mass and charge, E0=30
kV/cm is
the greatest possible electric field of ball lightning, leading to the electric
air discharge, c - the speed of light. In moist air maximum field strength
becomes smaller, which allows ball lightning have the sizes more than 34 cm.
According to the model under
different sizes of ball lightning its parameters are as follows: 1) radius of 7
cm, the current in the shell 2.9 • 10 3 A, the internal magnetic
field of 0.026 T, the energy of 503 J. 2) the radius of 1 cm, the current in
the shell 20 A, the internal magnetic field of 0.0013 T, the energy of 2.2 J.
It was confirmed by
investigations in the St. Petersburg Institute of Nuclear Physics, that the
ball lightning actually consists of positively charged ions and negatively
charged shell. [3] It was confirmed also the
presence of uncompensated electric charge at a ball lightning. [3]
Bead lightning is also explained
on the basis of electron-ionic model of ball lightning. [4]
[5]
References
- Fedosin S.G. Sovremennye
problemy fiziki: v poiskakh novykh printsipov. – Moskva.: Editorial URSS, 2002, 192
pp.
- Fedosin S.G., Kim A.S. The
Physical Theory of Ball Lightning. Applied Physics (Russian Journal) ,
No. 1, 2001, P. 69 – 87.
- Ball
lightning with his hands
- Sergey Fedosin, The
physical theories and infinite hierarchical nesting of matter, Volume
1, LAP LAMBERT Academic Publishing, pages: 580, ISBN-13: 978-3-659-57301-9.
- Fedosin
S.G. Electron-ion model of ball and bead lightning. Journal of Atmospheric
and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, Vol. 265, 106374 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jastp.2024.106374.
External links
- Kim
A.S. and Fedosin S.G. Method of production of ball lightning // Patent of
the Russian Federation No. 2210195, class 7H05H1/00, G09B23/18, bulletin
No. 22, 2003.
- Sergey
G. Fedosin, Anatolii S. Kim. Electron-Ionic Model of
Ball Lightening. Journal of new energy, V. 6, No. 1, 2001, P. 11 - 18.
- Electron-ionic
model of ball lightning in Russian
- Ball Lightning as
electromagnetic tor with NO
- Grani.ru
- Ricky Polser
Videos Films, depicting the fireballs (in Russian)
- Amateur shooting a
fireball